JavaScript 空間坐標(biāo)的使用
基礎(chǔ)知識
首先參考畫布分為視口(窗口)與文檔的含義
網(wǎng)頁很多都是多屏,所以文檔尺寸一般大于視口尺寸
視口尺寸不包括瀏覽器工具條、菜單、標(biāo)簽、狀態(tài)欄等
當(dāng)打開控制臺后,視口尺寸相應(yīng)變小
文檔像 position 定位,視口類似 fixed 定位
文檔坐標(biāo)在頁面滾動時不發(fā)生改變
視口坐標(biāo)的操作需要考慮滾動條的位置
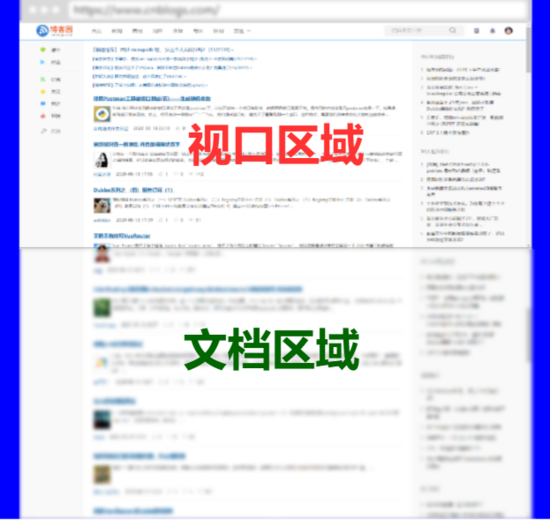
視口文檔
視口坐標(biāo)需要知道滾動條位置才可以進行計算,有以下幾種方式獲取滾動位置
方法 說明 注意 window.innerWidth 視口寬度 包括滾動條(不常用) window.innerHeight 視口高度 包括滾動條(不常用) document.documentElement.clientWidth 視口寬度 document.documentElement.clientHeight 視口高度
注意,均是以像素為單位,且視口尺寸不包括瀏覽器工具條、菜單、標(biāo)簽、狀態(tài)欄等
<script> document.write(document.documentElement.clientWidth); // 1707 document.write(document.documentElement.clientHeight) // 803 </script>
幾何形狀
元素在頁面中擁有多個描述幾何數(shù)值的尺寸,下面截圖進行了形象的描述。
方法 說明 備注 element.getBoundingClientRect 返回元素在視口坐標(biāo)及元素大小,不包括外邊距,width/height與offsetWidth/offsetHeight匹配 窗口坐標(biāo) element.getClientRects 行級元素每行尺寸位置組成的數(shù)組 element.offsetParent 擁有定位屬性的父級,或body/td/th/table 對于隱藏元素/body/html值為null element.offsetWidth 元素寬度尺寸,包括內(nèi)邊距與邊框和滾動條 element.offsetHeight 元素高度尺寸,包括內(nèi)邊距與邊框和滾動條 element.offsetLeft 相對于祖先元素的X軸坐標(biāo) element.offsetTop 相對于祖先元素的Y軸坐標(biāo) element.clientWidth 元素寬度,不包含邊框,只包含內(nèi)容和內(nèi)邊距,行元素尺寸為0 element.clientHeight 元素高度,不包含邊框,只包含內(nèi)容和內(nèi)邊距,行元素尺寸為0 element.clientLeft 內(nèi)容距離外部的距離,滾動條在左側(cè)時包括滾動條尺寸 element.clientTop 內(nèi)容距離頂部的距離,滾動條在頂部時包括滾動條尺寸 element.scrollWidth 元素寬度,內(nèi)容+內(nèi)邊距+內(nèi)容溢出的尺寸 element.scrollHeight 元素高度,內(nèi)容+內(nèi)邊距+內(nèi)容溢出的尺寸 element.scrollLeft 水平滾動條左側(cè)已經(jīng)滾動的寬度 element.scrollTop 垂直滾動條頂部已經(jīng)滾動的高度
為什么不要使用getComputedStyle
尺寸設(shè)置 auto 時獲取結(jié)果不可用
由于滾動條的存在,不同瀏覽器返回結(jié)果不同
元素沒有設(shè)置尺寸獲取不到
getBoundingClientRect
使用 getBoundingClientRect 獲取元素矩形信息
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang='en'><head> <meta charset='UTF-8'> <meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'> <title>Document</title> <style> div{ height: 300px; width: 300px; padding:10px; margin: 10px; border:5px solid #ddd; overflow: hidden; } </style></head><body> <div></div> </body><script> let div = document.querySelector('div'); let position = div.getBoundingClientRect(); console.log(position);</script></html>
計算結(jié)果的矩形尺寸不包括外邊距
bottom: 340height: 330left: 18right: 348top: 10width: 330x: 18y: 10
getClientRects
多行元素分別返回每行所占的尺寸,下面的行元素將為每行返回矩形尺寸
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang='en'><head> <meta charset='UTF-8'> <meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'> <title>Document</title> <style> span { width: 200px; overflow: auto; } </style></head><span>網(wǎng)頁很多都是多屏,所以文檔尺寸一般大于視口尺寸,當(dāng)打開控制臺后,視口尺寸相應(yīng)變小。網(wǎng)頁很多都是多屏,所以文檔尺寸一般大于視口尺寸,當(dāng)打開控制臺后,視口尺寸相應(yīng)變小。網(wǎng)頁很多都是多屏,所以文檔尺寸一般大于視口尺寸,當(dāng)打開控制臺后,視口尺寸相應(yīng)變小。</span><script> let span = document.querySelector(’span’) let info = span.getClientRects() console.log(info)</script></html>
// 第一行信息bottom: 29.33333396911621height: 21.33333396911621left: 8right: 1683.5555419921875top: 8width: 1675.5555419921875x: 8y: 8
// 第二行信息bottom: 50.66666793823242height: 21.33333396911621left: 8right: 264top: 29.33333396911621width: 256x: 8y: 29.33333396911621
坐標(biāo)判斷
Js 提供了方法獲取指定坐標(biāo)上的元素,如果指定坐標(biāo)點在視口外,返回值為 null
坐標(biāo)都是從左上角計算,這與 CSS 中的 right/bottom 等不同
窗口坐標(biāo)類似于 position:fixed
文檔坐標(biāo)類似于 position:absolute
方法 說明 element.elementsFromPoint 返回指定坐標(biāo)點所在的元素集合 element.elementFromPoint 返回指定坐標(biāo)點最頂級的元素
元素集合
返回指定坐標(biāo)點上的元素集合
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang='en'><head> <meta charset='UTF-8'> <meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'> <title>Document</title> <style> div{ width: 100px; height: 100px; } </style></head><body> <div></div></body><script> let positionEleList = document.elementsFromPoint(100,100); console.log(positionEleList); // div // body // html </script></html>
頂級元素
返回坐標(biāo)點上的頂級元素
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang='en'><head> <meta charset='UTF-8'> <meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'> <title>Document</title> <style> div{ width: 100px; height: 100px; } </style></head><body> <div></div></body><script> let positionEle = document.elementFromPoint(100,100); console.log(positionEle); // div</script></html>
滾動控制
方法 說明 參數(shù)說明 window.pageXOffset 文檔相對窗口水平滾動的像素距離 window.pageYOffset 文檔相對窗口垂直滾動的像素距離 element.scrollLeft() 元素X軸滾動位置 element.scrollTop() 元素Y軸滾動位置 element.scrollBy() 按偏移量進行滾動內(nèi)容 參數(shù)為對象,{top:垂直偏移量,left:水平偏移量,behavior:’滾動方式’} element.scroll() 或 element.scrollTo() 滾動到指定的具體位置 參數(shù)為對象,{top:X軸文檔位置,left:Y軸文檔位置,behavior:’滾動方式’} element.scrollLeft 獲取和設(shè)置元素X軸滾動位置 這是屬性,設(shè)置X軸文檔位置 element.scrollTop 獲取和設(shè)置元素Y軸滾動位置 這是屬性,設(shè)置Y軸文檔位置 element.scrollIntoView(bool) 定位到頂部或底部 參數(shù)為true元素定位到頂部,為false定位到窗口底部
使用 scrollBy 滾動文檔
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang='en'><head> <meta charset='UTF-8'> <meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'> <title>Document</title> <style> body { height: 2000px; background: linear-gradient(to bottom, red, green, blue, yellow) } </style></head><body></body><script> setInterval(() => { document.documentElement.scrollBy({top:30,behavior:'smooth'},100); // 相當(dāng)于每個3秒往下走30px,參照于上次所停留位置,smooth平滑滾動 },3000);</script></html>
使用 scroll 滾動到指定位置
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang='en'><head> <meta charset='UTF-8'> <meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'> <title>Document</title> <style> body { height: 2000px; background: linear-gradient(to bottom, red, green, blue, yellow) } </style></head><body></body><script> setInterval(() => { document.documentElement.scroll({top:30,behavior:'smooth'},100); },3000); // 按照絕對位置,距離上部30px,只走一次,smooth平滑滾動</script></html>
使用元素 scrollIntoView 方法實現(xiàn)滾動操作,參數(shù)可以是布爾值或?qū)ο蟆?/p>
與 <a> 標(biāo)簽錨點效果類似。
參數(shù)為 true 時頂部對齊,相當(dāng)于 {block: 'start'}
參數(shù)為 false 時底部對齊,相當(dāng)于 {block: 'end'}
定義 {behavior:smooth} 為平滑滾動
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang='en'><head> <meta charset='UTF-8'> <meta name='viewport' content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0'> <title>Document</title> <style> section { height: 2000px; background: linear-gradient(to bottom, red, green, blue, yellow) } body button { position: fixed; bottom: 10%; width: 100px; height: 30px; } body button:first-of-type { right: 5%; } body button:last-of-type { left: 5%; } </style></head><body> <header> <h1>頭部</h1> </header> <button class='top'>TOP</button> <button class='bottom'>BOTTOM</button> <section></section> <footer> <h1>底部</h1> </footer></body><script> document.querySelector('button.top').addEventListener('click', (event) => { let h1 = document.querySelector('header h1'); h1.scrollIntoView({ behavior: 'smooth', }) }); document.querySelector('button.bottom').addEventListener('click', (event) => { let h1 = document.querySelector('footer h1'); h1.scrollIntoView({ behavior: 'smooth', }) })</script></html>
到此這篇關(guān)于JavaScript 空間坐標(biāo)的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)JavaScript 空間坐標(biāo)內(nèi)容請搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:

 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備