詳解Spring中的Transactional屬性
聲明式事務(wù)管理建立在AOP之上的。其本質(zhì)是對(duì)方法前后進(jìn)行攔截,然后在目標(biāo)方法開始之前創(chuàng)建或者加入一個(gè)事務(wù),在執(zhí)行完目標(biāo)方法之后根據(jù)執(zhí)行情況提交或者回滾事務(wù)。
簡(jiǎn)而言之,@Transactional注解在代碼執(zhí)行出錯(cuò)的時(shí)候能夠進(jìn)行事務(wù)的回滾。

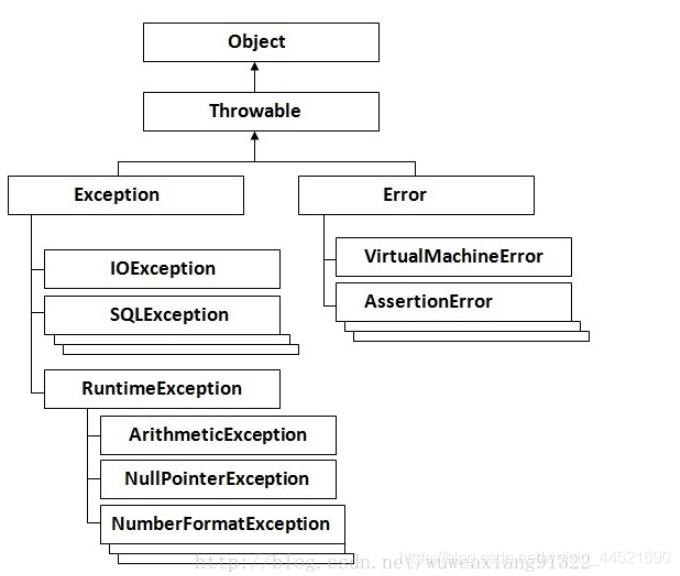
而至于什么是運(yùn)行時(shí)異常(RuntimeException),什么是非運(yùn)行時(shí)異常,可通過下圖所示理解(圖片截取網(wǎng)絡(luò))
正常情況下,只要在方法上添加@Transactional注解就完事了,但是需要注意的是,雖然使用簡(jiǎn)單,但是如果不合理地使用注解,還是會(huì)存在注解失效的問題。
@Transactional 應(yīng)用在非 public 修飾的方法上
事務(wù)攔截器在目標(biāo)方法執(zhí)行前后進(jìn)行攔截,內(nèi)部會(huì)調(diào)用方法來獲取Transactional 注解的事務(wù)配置信息,調(diào)用前會(huì)檢查目標(biāo)方法的修飾符是否為 public,不是 public則不會(huì)獲取@Transactional 的屬性配置信息。
@Transactional 注解屬性 rollbackFor 設(shè)置錯(cuò)誤
rollbackFor 可以指定能夠觸發(fā)事務(wù)回滾的異常類型。Spring默認(rèn)拋出了未檢查unchecked異常(繼承自 RuntimeException 的異常)或者 Error才回滾事務(wù);其他異常不會(huì)觸發(fā)回滾事務(wù)。如果在事務(wù)中拋出其他類型的異常,但卻期望 Spring 能夠回滾事務(wù),就需要指定rollbackFor屬性。
同一個(gè)類中方法調(diào)用,導(dǎo)致@Transactional失效
開發(fā)中避免不了會(huì)對(duì)同一個(gè)類里面的方法調(diào)用,比如有一個(gè)類Test,它的一個(gè)方法A,A再調(diào)用本類的方法B(不論方法B是用public還是private修飾),但方法A沒有聲明注解事務(wù),而B方法有。則外部調(diào)用方法A之后,方法B的事務(wù)是不會(huì)起作用的。這也是經(jīng)常犯錯(cuò)誤的一個(gè)地方。那為啥會(huì)出現(xiàn)這種情況?其實(shí)這還是由于使用Spring AOP代理造成的,因?yàn)橹挥挟?dāng)事務(wù)方法被當(dāng)前類以外的代碼調(diào)用時(shí),才會(huì)由Spring生成的代理對(duì)象來管理。
異常被你的 catch“吃了”導(dǎo)致@Transactional失效
如果你手動(dòng)的catch捕獲這個(gè)異常并進(jìn)行處理,事務(wù)管理器會(huì)認(rèn)為當(dāng)前事務(wù)應(yīng)該正常commit,就會(huì)導(dǎo)致注解失效,如果非要捕獲且不失效,就必須在代碼塊內(nèi)throw new Exception拋出異常。
數(shù)據(jù)庫引擎不支持事務(wù)
開啟事務(wù)的前提就是需要數(shù)據(jù)庫的支持,我們一般使用的Mysql引擎時(shí)支持事務(wù)的,所以一般不會(huì)出現(xiàn)這種問題。
開啟多線程任務(wù)時(shí),事務(wù)管理會(huì)受到影響
因?yàn)榫€程不屬于spring托管,故線程不能夠默認(rèn)使用spring的事務(wù),也不能獲取spring注入的bean在被spring聲明式事務(wù)管理的方法內(nèi)開啟多線程,多線程內(nèi)的方法不被事務(wù)控制。如下代碼,線程內(nèi)調(diào)用insert方法,spring不會(huì)把insert方法加入事務(wù)就算在insert方法上加入@Transactional注解,也不起作用。
@Service public class ServiceA { @Transactional public void threadMethod(){ this.insert(); System.out.println('main insert is over'); for(int a=0 ;a<3;a++){ ThreadOperation threadOperation= new ThreadOperation(); Thread innerThread = new Thread(threadOperation); innerThread.start(); } } public class ThreadOperation implements Runnable { public ThreadOperation(){ } @Override public void run(){ insert(); System.out.println('thread insert is over'); } } public void insert(){ //do insert...... } }
如果把上面insert方法提出到新的類中,加入事務(wù)注解,就能成功的把insert方法加入到事務(wù)管理當(dāng)中
@Service public class ServiceA { @Autowired private ServiceB serviceB; @Transactional public void threadMethod(){ this.insert(); System.out.println('main insert is over'); for(int a=0 ;a<3;a++){ ThreadOperation threadOperation= new ThreadOperation(); Thread innerThread = new Thread(threadOperation); innerThread.start(); } } public class ThreadOperation implements Runnable { public ThreadOperation(){ } @Override public void run(){ serviceB.insert(); System.out.println('thread insert is over'); } } public void insert(){ //do insert...... } } @Service public class ServiceB { @Transactional public void insert(){ //do insert...... } }
另外,使用多線程事務(wù)的情況下,進(jìn)行回滾,比較麻煩。thread的run方法,有個(gè)特別之處,它不會(huì)拋出異常,但異常會(huì)導(dǎo)致線程終止運(yùn)行。
最麻煩的是,在線程中拋出的異常即使在主線程中使用try…catch也無法截獲這非常糟糕,我們必須要“感知”到異常的發(fā)生。比如某個(gè)線程在處理重要的事務(wù),當(dāng)thread異常終止,我必須要收到異常的報(bào)告,才能回滾事務(wù)。這時(shí)可以使用線程的UncaughtExceptionHandler進(jìn)行異常處理,UncaughtExceptionHandler名字意味著處理未捕獲的異常。更明確的說,它處理未捕獲的運(yùn)行時(shí)異常。
如下代碼線程出要使用①處要拋出異常②處要捕捉異常,并且要拋出RuntimeException③處手動(dòng)處理回滾邏輯
@Service public class ServiceA { @Autowired private ServiceB serviceB; @Transactional public void threadMethod(){ this.insert(); System.out.println('main insert is over'); for(int a=0 ;a<3;a++){ ThreadOperation threadOperation= new ThreadOperation(); Thread innerThread = new Thread(threadOperation); innerThread.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(new Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler() { public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) { try { serviceB.delete();③ } catch (Exception e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } } }); innerThread.start(); } } public class ThreadOperation implements Runnable { public ThreadOperation(){ } @Override public void run(){ try { serviceB.insert(); }catch (Exception ex){ ② System.out.println(' Exception in run '); throw new RuntimeException(); } System.out.println('thread insert is over'); } } public void insert(){ //do insert...... } } @Service public class ServiceB { @Transactional public void insert() throws Exception{ ① //do insert...... } @Transactional public void delete() throws Exception{ //do delete...... } }
到此這篇關(guān)于詳解Spring中的Transactional屬性的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Transactional屬性詳解內(nèi)容請(qǐng)搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:
1. html清除浮動(dòng)的6種方法示例2. phpstudy apache開啟ssi使用詳解3. JavaScript中常見的幾種獲取元素的方式4. ASP.NET MVC使用異步Action的方法5. Xml簡(jiǎn)介_動(dòng)力節(jié)點(diǎn)Java學(xué)院整理6. jsp實(shí)現(xiàn)登錄驗(yàn)證的過濾器7. jsp文件下載功能實(shí)現(xiàn)代碼8. uni-app結(jié)合.NET 7實(shí)現(xiàn)微信小程序訂閱消息推送9. AJAX的跨域問題解決方案10. ajax實(shí)現(xiàn)頁面的局部加載
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備