詳解Java中CountDownLatch異步轉(zhuǎn)同步工具類
由于公司業(yè)務(wù)需求,需要對(duì)接socket、MQTT等消息隊(duì)列。眾所周知 socket 是雙向通信,socket的回復(fù)是人為定義的,客戶端推送消息給服務(wù)端,服務(wù)端的回復(fù)是兩條線。無法像http請(qǐng)求有回復(fù)。下發(fā)指令給硬件時(shí),需要校驗(yàn)此次數(shù)據(jù)下發(fā)是否成功。用戶體驗(yàn)而言,點(diǎn)擊按鈕就要知道此次的下發(fā)成功或失敗。
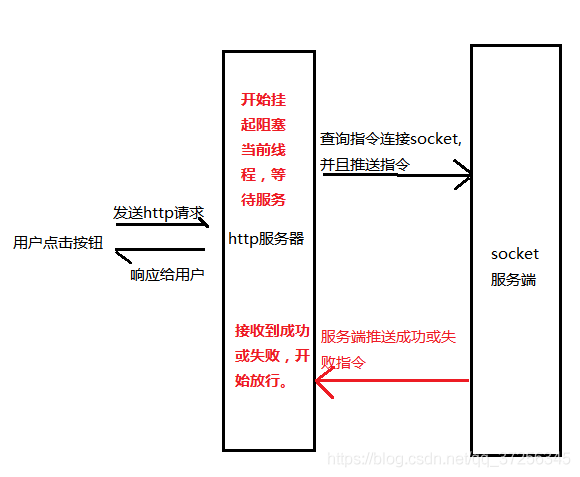
如上圖模型,
第一種方案使用Tread.sleep優(yōu)點(diǎn):占用資源小,放棄當(dāng)前cpu資源缺點(diǎn): 回復(fù)速度快,休眠時(shí)間過長,仍然需要等待休眠結(jié)束才能返回,響應(yīng)速度是固定的,無法及時(shí)響應(yīng)第二種方案使用CountDownLatch
package com.lzy.demo.delay;import java.util.Map;import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class CountDownLatchPool { //countDonw池 private final static Map<Integer, CountDownLatch> countDownLatchMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); //延遲隊(duì)列 private final static DelayQueue<MessageDelayQueueUtil> delayQueue = new DelayQueue<>(); private volatile static boolean flag =false; //單線程池 private final static ExecutorService t = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1)); public static void addCountDownLatch(Integer messageId) {CountDownLatch countDownLatch = countDownLatchMap.putIfAbsent(messageId,new CountDownLatch(1) );if(countDownLatch == null){ countDownLatch = countDownLatchMap.get(messageId);}try { addDelayQueue(messageId); countDownLatch.await(3L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);} catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println('阻塞等待結(jié)束~~~~~~'); } public static void removeCountDownLatch(Integer messageId){CountDownLatch countDownLatch = countDownLatchMap.get(messageId);if(countDownLatch == null) return;countDownLatch.countDown();countDownLatchMap.remove(messageId);System.out.println('清除Map數(shù)據(jù)'+countDownLatchMap); } private static void addDelayQueue(Integer messageId){delayQueue.add(new MessageDelayQueueUtil(messageId));clearMessageId(); } private static void clearMessageId(){synchronized (CountDownLatchPool.class){ if(flag){return; } flag = true;}t.execute(()->{ while (delayQueue.size() > 0){System.out.println('進(jìn)入線程并開始執(zhí)行');try { MessageDelayQueueUtil take = delayQueue.take(); Integer messageId1 = take.getMessageId(); removeCountDownLatch(messageId1); System.out.println('清除隊(duì)列數(shù)據(jù)'+messageId1);} catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace();} } flag = false; System.out.println('結(jié)束end----');}); } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {/*測試超時(shí)清空mapnew Thread(()->addCountDownLatch(1)).start();new Thread(()->addCountDownLatch(2)).start();new Thread(()->addCountDownLatch(3)).start();*///提前創(chuàng)建線程,清空countdownnew Thread(()->{ try {Thread.sleep(500L);removeCountDownLatch(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace(); }}).start();//開始阻塞addCountDownLatch(1); //通過調(diào)整上面的sleep我們發(fā)現(xiàn)阻塞市場取決于countDownLatch.countDown()執(zhí)行時(shí)間 System.out.println('阻塞結(jié)束----'); }}class MessageDelayQueueUtil implements Delayed { private Integer messageId; private long avaibleTime; public Integer getMessageId() {return messageId; } public void setMessageId(Integer messageId) {this.messageId = messageId; } public long getAvaibleTime() {return avaibleTime; } public void setAvaibleTime(long avaibleTime) {this.avaibleTime = avaibleTime; } public MessageDelayQueueUtil(Integer messageId){this.messageId = messageId;//avaibleTime = 當(dāng)前時(shí)間+ delayTime//重試3次,每次3秒+1秒的延遲this.avaibleTime=3000*3+1000 + System.currentTimeMillis(); } @Override public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {long diffTime= avaibleTime- System.currentTimeMillis();return unit.convert(diffTime,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } @Override public int compareTo(Delayed o) {//compareTo用在DelayedUser的排序return (int)(this.avaibleTime - ((MessageDelayQueueUtil) o).getAvaibleTime()); }}
由于socket并不確定每次都會(huì)有數(shù)據(jù)返回,所以map的數(shù)據(jù)會(huì)越來越大,最終導(dǎo)致內(nèi)存溢出需定時(shí)清除map內(nèi)的無效數(shù)據(jù)。可以使用DelayedQuene延遲隊(duì)列來處理,相當(dāng)于給對(duì)象添加一個(gè)過期時(shí)間
使用方法 addCountDownLatch 等待消息,異步回調(diào)消息清空removeCountDownLatch
到此這篇關(guān)于詳解Java中CountDownLatch異步轉(zhuǎn)同步工具類的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)CountDownLatch異步轉(zhuǎn)同步工具類內(nèi)容請(qǐng)搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:
1. php使用正則驗(yàn)證密碼字段的復(fù)雜強(qiáng)度原理詳細(xì)講解 原創(chuàng)2. 基于javaweb+jsp實(shí)現(xiàn)企業(yè)車輛管理系統(tǒng)3. HTML5實(shí)戰(zhàn)與剖析之觸摸事件(touchstart、touchmove和touchend)4. ASP將數(shù)字轉(zhuǎn)中文數(shù)字(大寫金額)的函數(shù)5. Jsp servlet驗(yàn)證碼工具類分享6. jscript與vbscript 操作XML元素屬性的代碼7. 基于PHP做個(gè)圖片防盜鏈8. Jsp+Servlet實(shí)現(xiàn)文件上傳下載 文件列表展示(二)9. asp.net core 認(rèn)證和授權(quán)實(shí)例詳解10. XML在語音合成中的應(yīng)用
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備